Understanding T4 Spine Pain: Causes, Treatment, and Management
The human spine is a remarkable structure, providing support and flexibility to the body while housing the spinal cord, which is pivotal for carrying nerve signals. One of the less discussed aspects of spinal health is the pain that can occur around the T4 vertebra. This article delves into the multifaceted topic of t4 spine pain, exploring its symptoms, potential causes, and the most effective treatment options available.
What is the T4 Vertebra?
The T4 vertebra is the fourth thoracic vertebra, located in the upper back region of the spine. The thoracic spine consists of 12 vertebrae, collectively labeled T1 to T12. Each vertebra serves a crucial role in protecting the spinal cord and supporting the upper body. The T4 vertebra is particularly important as it connects to the ribs, contributing to the stability and mobility of the thoracic cage.
Common Symptoms of T4 Spine Pain
T4 spine pain can present a range of symptoms that vary from mild discomfort to debilitating pain. Understanding these symptoms is the first step in identifying the underlying issue. Common symptoms include:
- Localized Pain: Pain that is felt directly over the T4 vertebra or surrounding regions.
- Radiating Pain: Discomfort that extends from the T4 area to the shoulders, neck, or down the arms.
- Muscle Spasms: Involuntary contractions of the muscles surrounding the thoracic spine, contributing to discomfort.
- Postural Issues: Difficulty maintaining proper posture, which can lead to further pain and discomfort.
- Numbness or Tingling: Sensations that might radiate along the nerves extending from the T4 level.
Causes of T4 Spine Pain
Understanding the causes of t4 spine pain is essential in developing an effective treatment plan. Several factors can contribute to the development of pain in this area:
- Muscle Strain: Overexertion or improper lifting techniques can strain the muscles around the T4 vertebra, causing pain.
- Injuries: Trauma from accidents, falls, or sports injuries can directly affect the T4 region.
- Herniated Discs: Bulging or ruptured discs can press on nearby nerves, resulting in pain and discomfort.
- Osteoarthritis: This degenerative condition can affect the joints between the vertebrae, leading to inflammation and pain.
- Scoliosis: Abnormal curvature of the spine can place additional stress on the T4 region.
- Structural Disorders: Congenital conditions or diseases that affect bone health can lead to pain in the thoracic spine.
Diagnosis of T4 Spine Pain
Diagnosing t4 spine pain typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional, often a chiropractor or orthopedic specialist. The diagnostic process may include:
- Physical Examination: The doctor assesses posture, range of motion, and identifies specific pain points.
- Medical History: Understanding previous injuries, lifestyle habits, and family medical history aids in diagnosis.
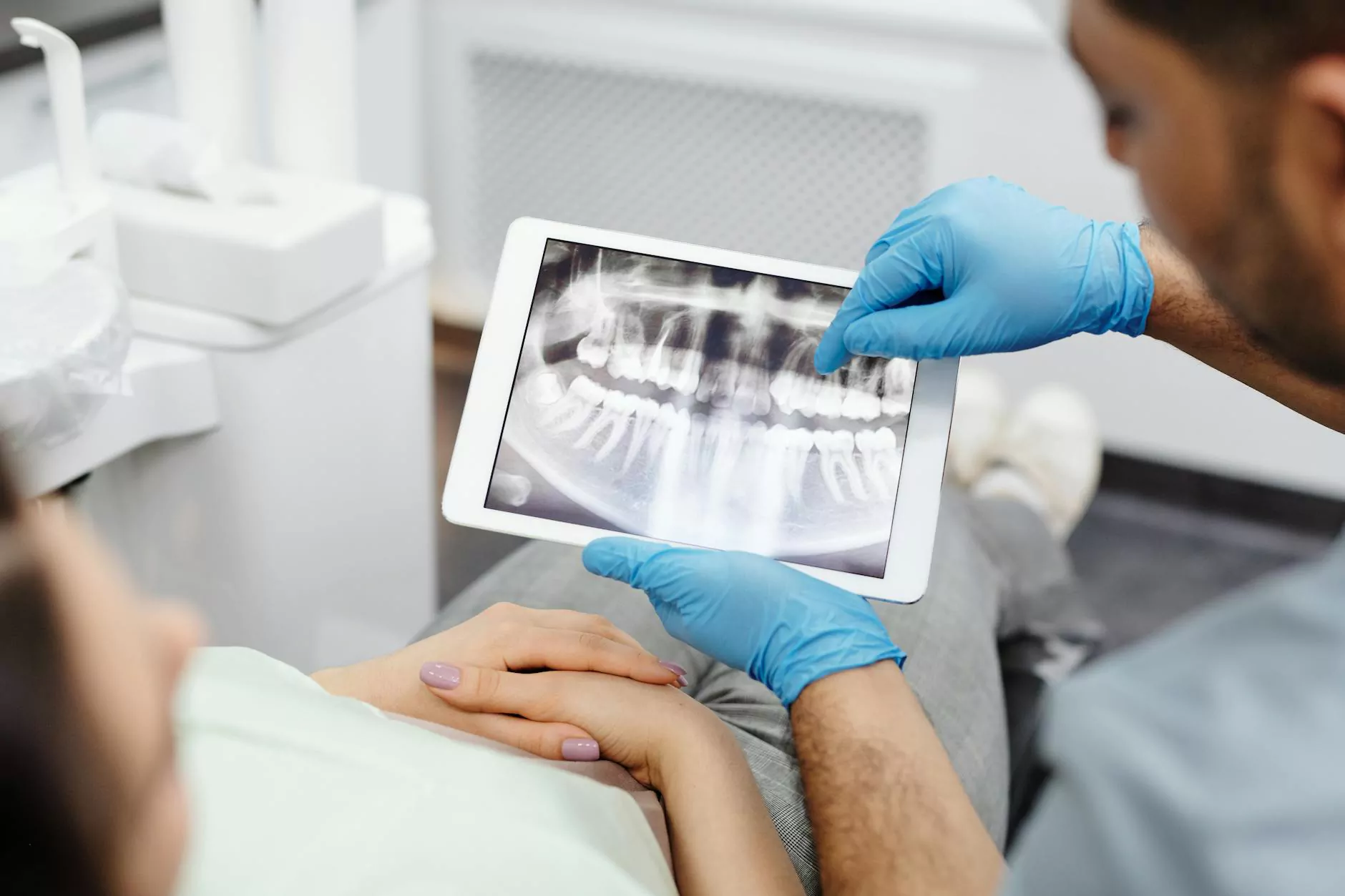
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans may be recommended to visualize the structures of the spine.
Treatment Options for T4 Spine Pain
Once a diagnosis is established, several treatment options can help alleviate t4 spine pain. These treatments often aim to relieve pain, improve mobility, and restore normal function.
Conservative Treatments
Most cases of T4 spine pain can be managed with conservative treatments, including:
- Rest: Allowing the body to recover is crucial. Avoiding activities that exacerbate pain is recommended.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can develop a specific exercise program to strengthen the muscles around the spine and improve flexibility.
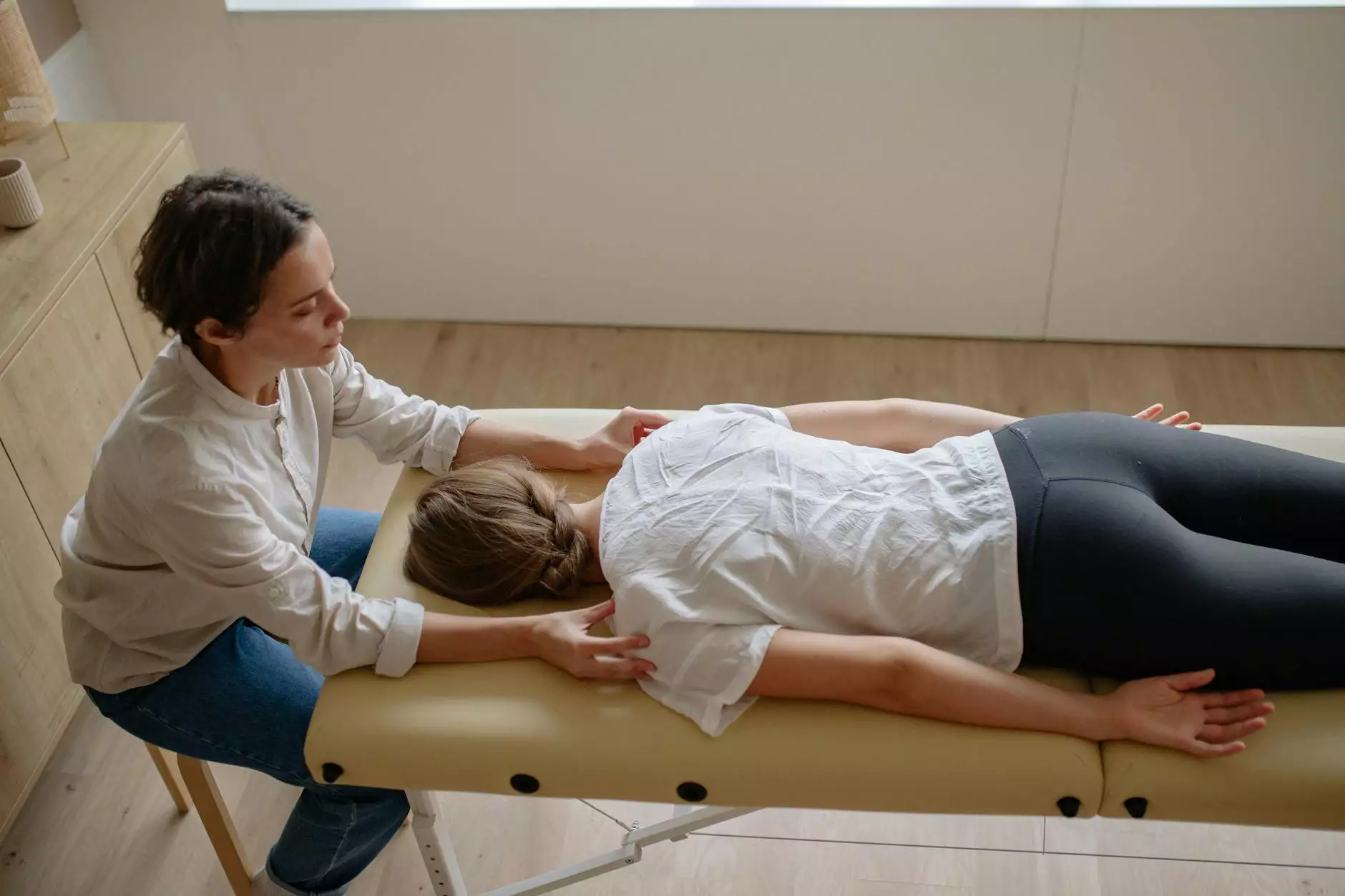
- Chiropractic Adjustments: Chiropractors often use spinal manipulations to align the vertebrae, alleviate pressure on nerves, and enhance mobility.
- Heat and Ice Therapy: Application of heat can soothe stiff muscles, while ice can reduce inflammation and numb acute pain.
- Medications: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Advanced Treatment Options
If conservative treatments fail to provide relief, more advanced interventions may be necessary:
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections can be administered to reduce inflammation directly to the affected area.
- Physical modalities: Techniques such as electrotherapy or ultrasound can be utilized to alleviate pain.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required to address underlying structural issues, such as herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
Preventing T4 Spine Pain
Preventative measures play a crucial role in reducing the likelihood of developing t4 spine pain. Adopting a proactive approach can safeguard your spinal health.
Ergonomic Practices
Ensure that your workspace is set up ergonomically to minimize strain on your back:
- Chair Support: Use a chair that promotes proper posture with adequate lumbar support.
- Monitor Height: Position your computer monitor at eye level to prevent neck strain.
- Frequent Breaks: Take regular breaks from sitting to stretch and move around.
Regular Exercise
Incorporate regular physical activity that strengthens back muscles, improves core stability, and maintains flexibility. Recommended exercises include:
- Core Strengthening: Exercises such as planks and abdominal crunches.
- Flexibility Training: Yoga and stretching routines can significantly improve spinal flexibility.
- Aerobic Activities: Walking, swimming, and cycling promote overall fitness without overstraining the back.
Chiropractic Care and the Role of Chiropractors
Chiropractors specialize in diagnosing and treating spinal disorders, including t4 spine pain. Their approach focuses on the relationship between the spine and nervous system, employing a variety of techniques to restore function and alleviate pain.
Chiropractic Techniques for Managing T4 Spine Pain
Chiropractors may use several techniques to treat T4 spine pain, including:
- Spinal Manipulation: Gentle adjustments are performed to correct misalignments in the spine.
- Myofascial Release: This technique alleviates tension in muscles and fascia, promoting relief from discomfort.
- Therapeutic Exercises: Customized exercise plans help strengthen the back and support recovery.
Conclusion: Embracing a Healthier Spine
Living with t4 spine pain can be challenging, but understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options empowers individuals to take control of their spinal health. Whether through conservative methods, chiropractic care, or preventative practices, effective management is within reach.
For those seeking more personalized advice or treatment options, consider reaching out to a chiropractic specialist at IAOM-US. By prioritizing spinal health and adopting an informed approach, you can enhance your quality of life and prevent future pain.
Resources for Further Reading
Here are some valuable resources to deepen your understanding of spinal health and chiropractic care:
- IAOM-US Official Website - Comprehensive information about chiropractic and physical therapy.
- Spine-Health.com - Articles and insights on spine disorders and treatments.
- Chiro.org - Resources for chiropractic professionals and patients.